Epoxy resin in the field of electrical and electronic applications are mainly: power transformers, transformers, insulators and other electrical appliances casting materials, electronic devices potting materials, integrated circuits and semiconductor components plastic sealing materials, circuit boards and copper-clad materials, electronic appliances insulation coatings, insulating adhesives, high-voltage insulator mandrel, high-voltage high-current switch in the insulation parts and other insulation structure materials.
The development direction of epoxy resin electronic and electrical packaging and insulation materials is mainly: to improve the heat resistance, electricity and flame retardancy of the material, and to reduce water absorption, shrinkage and internal stress. The main ways of improvement are: synthesis of new epoxy resins and curing agents; high purity of raw materials; modification of epoxy resins, including toughening, softening, filling, reinforcing, blending, etc.; development of bromine-free flame retardant systems; improvement of molding process methods, equipment and technology.
Epoxy Casting and Casting Materials
Epoxy casting is the process of pouring epoxy resin, curing agent and other matching materials into a set mold and cross-linking and curing the thermoplastic fluid into a hot lying product. Because of its excellent electrical and mechanical properties, epoxy resin casting has been widely used in the electrical industry and is developing rapidly.
There are different ways of distinguishing the process of epoxy resin casting, understood in terms of different process conditions. From the way the material enters the mold it can be divided into pouring and pressing. Pouring refers to the self-flow of material into the mold. It is also divided into normal pressure pouring and vacuum pouring. Pressing means that the material enters the mold under external pressure, and in order to force the shrinkage, the external pressure is maintained during the material curing process.
From the material curing temperature to distinguish can be divided into normal temperature pouring method and high temperature pouring method. The choice of normal or high temperature casting method is determined by the nature of the casting material itself, the fundamental difference being the temperature conditions necessary for the curing process of the casting material.
The speed at which the material cures can be differentiated into the normal curing method and the fast-curing method. The time required from the entry of the material into the mold to the removal of the mold is the initial curing time, which takes several hours or even a dozen hours for the ordinary curing method, but only ten minutes to a few minutes for the rapid curing method.
The modern casting process, the application of more mature casting process methods are mainly vacuum casting method and automatic pressure gel method.
Vacuum Casting Process
The vacuum casting process is currently the most widely used and mature method of epoxy resin casting.
For an electrical insulation product cast in epoxy resin, it requires perfect appearance, dimensional stability, mechanical and electrical properties. These properties depend on the design of the part itself, the quality of the mold, the choice of the casting material and the control of the casting process. The technical point of epoxy resin vacuum casting is to reduce as much as possible the air gaps and bubbles in the cast product. In order to achieve this, it is necessary to control the vacuum skin, the temperature and the process time in all processes such as pre-treatment of raw materials, mixing and casting.
Automatic pressure gelation process
The automatic pressure gelation process is a technology developed by the Swiss company CIB into City in the early 1970s. It is also known as the pressure injection process because it is similar to the injection molding process for thermoplastics. The most significant advantage of this process is that it significantly increases the efficiency of the pouring process. The successful development and industrial application of automatic pressure gelation is a revolution in the development of vacuum pouring from intermittent, manual operations to automated production, with the main differences between it and vacuum pouring being.
1) The casting material is injected into the mold under external pressure through the injection port via a pipe.
2) The mixing temperature of the material is low and the mold temperature is high.
3) After the material has been injected into the mold, the curing speed is fast, usually from ten minutes to several minutes.
4)The mold is fixed to the hydraulic press and the heating of the mold is provided by an electric heater on the mold or mold fixing plate.
5) The molds are closed and dismantled by the movement of the mold fixing plate on the hydraulic press.
Features of the automatic pressure gel process: high mold utilization, short production cycle, high labor efficiency; low degree of damage during mold loading and unloading, long service life of molds; high degree of automation, light labor intensity of operators; good product formability and improved product quality.
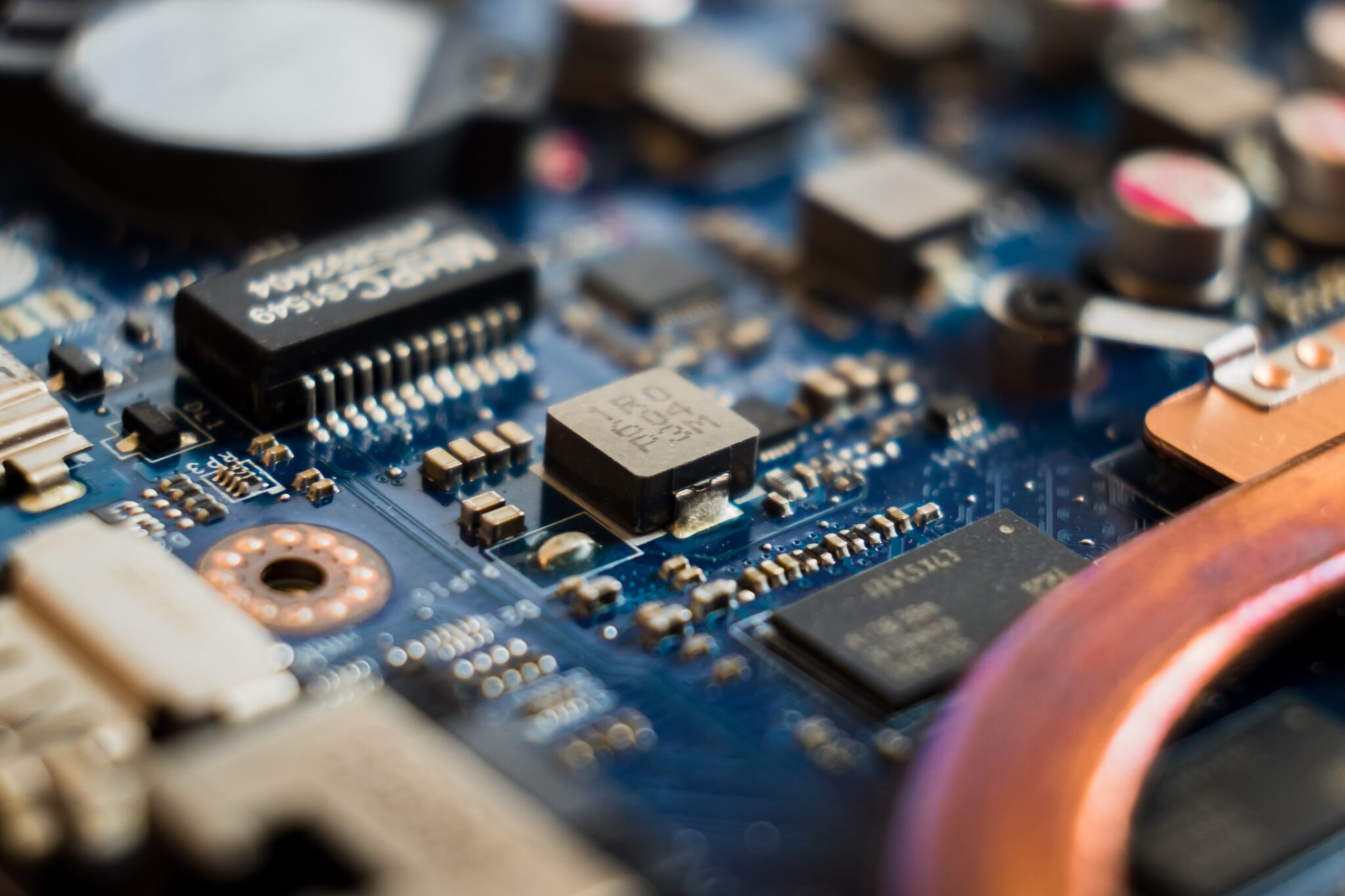
Potting and potting materials for epoxy resins
- Uses of potting materials
Potting is an important application area for epoxy resins. It is widely used in the electronic device manufacturing industry and is an indispensable and important insulating material for the electronics industry.
- Uses of potting materials
Potting is an important application area for epoxy resins. It is widely used in the electronic device manufacturing industry and is an indispensable and important insulating material for the electronics industry.
Potting is the mechanical or manual infusion of liquid epoxy resin compound into the device with electronic components and circuits, curing at room temperature or under heating conditions to become a thermal polymer insulation material with excellent performance. Its function is: to strengthen the integrity of electronic devices, to improve the resistance to external shocks and vibrations; to improve the insulation between internal components and lines, which is conducive to the miniaturization and lightweighting of devices; to avoid direct exposure of components and lines, and to improve the waterproof and moisture-proof performance of devices.
Classification of potting compounds
Epoxy potting compounds have a wide range of applications and a wide variety of technical requirements. In terms of curing conditions, there are two types: room temperature curing and heating curing. In terms of dosage form, there are two types of two-component and one-component. Multi-component formulations are not often seen as commodities due to the inconvenience of using them.
Room temperature curing epoxy potting material is generally two-component, after potting without heating can be cured, the equipment requirements are not high, easy to use. The disadvantage is that the compound work teaching degree is large, poor permeability, applicable period is short, it is difficult to realize automatic production, and the curing material heat resistance and electrical properties are not very high. Generally used for low pressure electronic devices potting or not suitable for heating curing occasions.
More Epoxy resin Electronics & Insulation applications, please contact us via email: sales@yqxpolymer.com, or voice to us at: +86-28-8411-1861.
Some pictures and texts are reproduced from the Internet, and the copyright belongs to the original author. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete.



